Turbine Refurbish Contract Expected to Save Navy Millions
The U.S. Navy projects saving of more than $100 million over the next five years following a contract award to refurbish propulsion gas turbine parts for surface combatants, the command announced July 19.
Naval Surface Warfare Center, Philadelphia Division (NSWCPD), a Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA) field activity, awarded the contract to leverage and expand existing affordability and innovation initiatives - key NAVSEA enablers to maintaining the Navy's ships and ensuring the necessary funds are available to build the next generation of naval vessels.
Previously, the Navy was required to use new turbine blades and nozzles, known as the engine's high pressure "hot section kit," during an engine's rebuild. A substantial cost increase of these new parts led NSWCPD to seek alternatives.
According to John Viercinski, NSWC PD surface combatant and gas turbine engineering team lead, the new kits cost over $1 million, while refurbished kits only cost approximately $200,000.
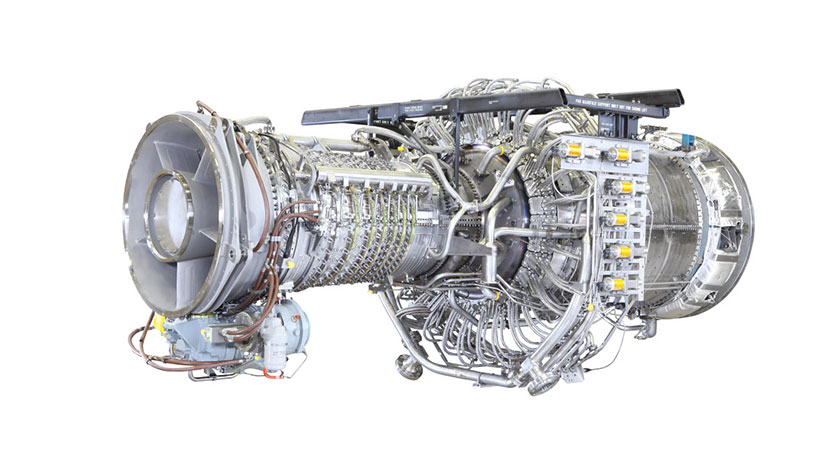
The contract allows the Navy to supply commercial and government repair vendors with refurbished high pressure turbine parts to create overhaul kits for two different configurations of LM2500 turbines. These engine configurations, the Single Shank Turbines (SST) and the Paired Blade Turbines (PBT), are responsible for the propulsion of all Navy destroyers and cruisers, as well as half of its littoral combat ships, a total of 372 engines.
"The LM2500 is the Navy's most common propulsion engine," Viercinski said. "It is the heart of the surface fleet's propulsion."
The LM2500 SST is the main propulsion marine gas turbine (MGT) used in the Arleigh Burke class destroyer and the Independence-variant Littoral Combat Ship class. The LM2500 PBT is the main propulsion unit for the Cruiser class.
Over the course of a ship engine's lifecycle, heat and thermal wear cause the turbine blades and nozzles to lose their protective coating. Loss of parent metal for these turbine components is also possible. Turbine component degradation is one of the reasons engines are ultimately removed from ships.
At the end of an engine's service life the Navy removes the engine from the ship and replaces it with a ready-for-issue engine. LM2500 engines are overhauled at Naval Air Systems Command's (NAVAIR) Fleet Readiness Center Southwest (FRCSW). During the overhaul process, engines are completely disassembled and subjected to an extensive inspection and rebuild process, utilizing new and refurbished materials.
"We worked hand-in-hand with NSWCPD's Propulsion Systems Division to develop the acquisition strategy and refine the statement of work," said Contracting Officer Kevin Hann. "We worked with legal counsel to develop the source selection strategy."
The contract's biggest win is ability now to rebuild engines using refurbished hot section kits instead of purchasing those parts new.
"Based upon our pricing calculator for this contract, $27 million could produce 100 SST hot section kits and 50 PBT hot section kits," said Matthew Driscoll, the lead LM2500 mechanical engineer for NSWCPD. "That's a conservative projected cost savings to the taxpayers of $103 million over 5 years as compared to the new part cost."
By Keegan Rammel and Matt Leonard, NSWC Philadelphia public affairs.

